What is Histamine?
Histamine (1) is an important bio-active chemical involved in your immune system, digestive system, and your central nervous system. Histamine is found in your mast cells (white blood cells). As a neurotransmitter, it communicates important messages from your body to the brain. It is also a component of stomach acid, which is what helps you break down food in your stomach. It also helps you move your bowels, pay attention and enhance exercise.
Histamine Release
Histamine is released by mast cells. Mast cells are found in all human tissues, especially at places where the body interfaces with the environment, like the gut and skin. Once Histamine is released there are receptors that bind with histamine to create important organ functions.
Histamine Receptors
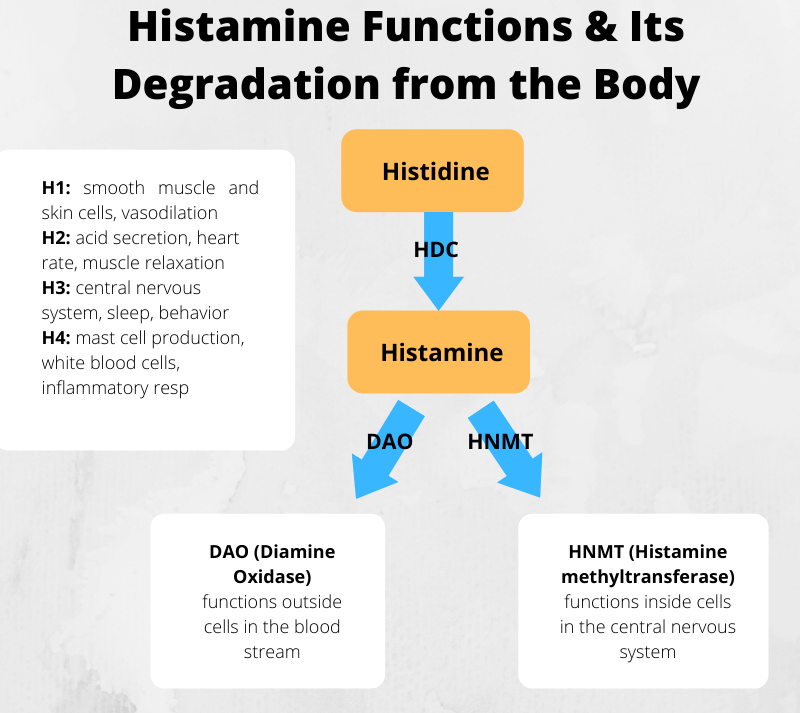
Histamine receptors are proteins situated in various parts of the body that bind with histamine to produce a specific effect on the organism. There are four known receptors, designated H1 – H4. The receptor that the histamine reacts with is dependent upon where the histamine is released in the body. Histamine receptors are located all over the body and have many important functions including (3):
- Histamine H1 receptors:Smooth muscle and endothelial cells affecting skin; blood vessels (Benadryl and Claritin block activity of these receptors)
- Histamine H2 receptors:Cells in the intestines control acid secretion, abdominal pain, and nausea; heart rate
- Histamine H3 receptors:Central nervous system controlling nerves, sleep, appetite and behaviour
- Histamine H4 receptors: Thymus, small intestine, spleen, colon, bone marrow and white blood cells; inflammatory response
One of the major effects of histamine is causing the blood vessels to swell and dilate. When the body senses that it is threatened it will secrete higher amounts of histamine. This allows the white blood cells to quickly move through the bloodstream and find the potential threat or infection. This is an important component to a healthy immune response.

Histamine Levels in Body
The ideal amount of histamine will allow the above functions to occur and occur perfectly. According to Dr. Joneja (4) who is an expert in this subject, Histamine levels of 0.3 to 1.0 nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL) in plasma are generally considered to be normal and each person will have a “threshold”. Histamine levels above that will cause symptoms to start appearing. Various abnormal physiological conditions, hormone changes, medications and gut imbalance can reduce the tolerance threshold of an individual.
How is Histamine Broken Down in the Body?
Histamine is broken down in your body through specific enzymes. In the central nervous system, it is metabolised by histamine N-methyltransferase (HMT), while in the digestive tract it is broken down by diamine oxidase (DAO).
DAO is the major enzyme involved in histamine metabolism. The enzyme converts the histamine into imidazole acetaldehyde which does not trigger any sort of reaction in the body. DAO is responsible for ensuring a steady histamine level required for the balance of numerous chemical reactions taking place in the body
Histamine Intolerance (HIT)
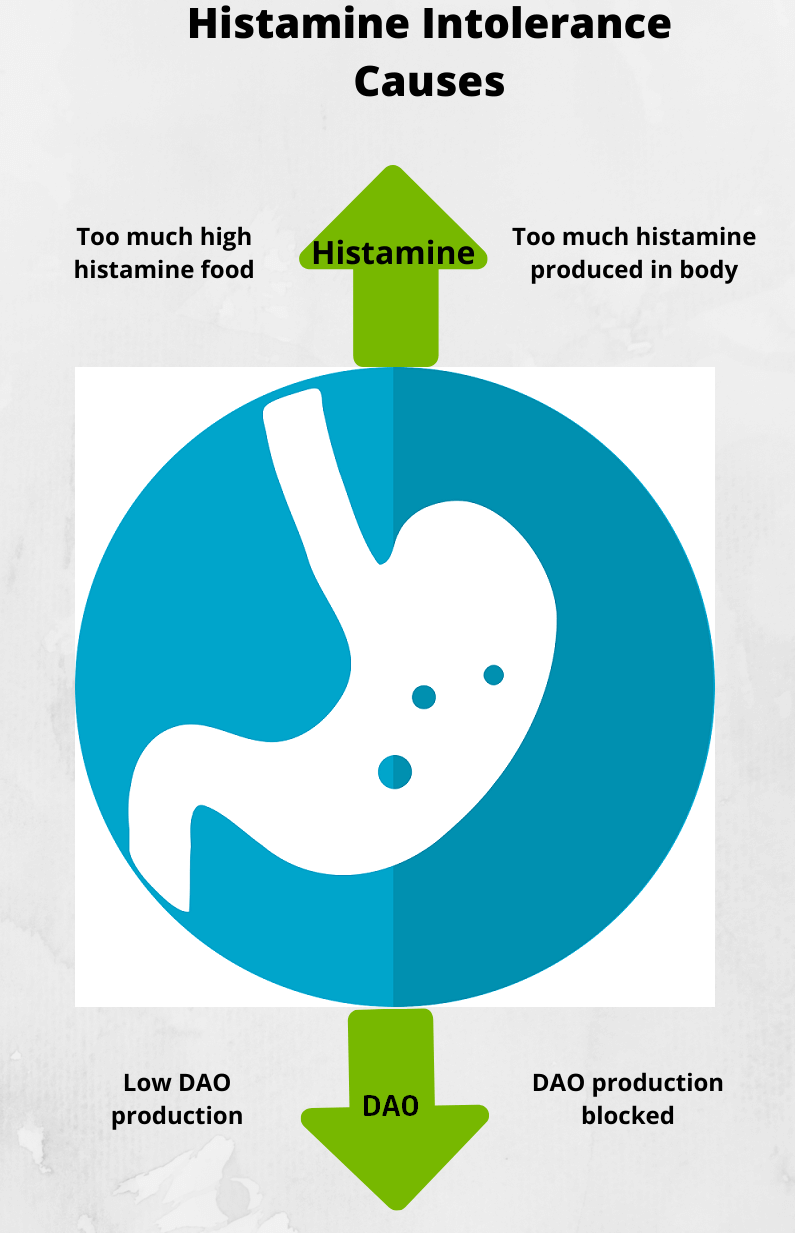
Generally, the body is able to breakdown histamine naturally and there is no “excess” levels of it to cause any adverse reaction. But for some people, they are unable to break down histamine effectively in their body or the histamine levels get too high which translates to “histamine intolerance” (2)
One way to explain how this works is to use the ‘histamine bucket’ explanation. Take a look at the illustration below. When you have histamine intolerance your bucket has a lower “capacity” and therefore it gets full faster. The symptoms you see are the result of the “histamine bucket” overflow.
According to research, impaired histamine degradation is the main cause of HIT. The body metabolizes histamine via two degradation pathways (also known as catabolism)
- Methylation by histamine-N-methyltransferase (HNMT)
- Oxidative degradation by diamine oxidase (DAO)
HNMT works on histamine in our cells while the enzyme DAO plays a major role in the breakdown of histamine in our gut. Studies have shown that it is a lack of DAO that is responsible for HIT in most cases and has received the most attention in medical research. Under normal circumstances, this enzyme will start degrading histamine to bring it back to normal levels, whereas in HIT the rate of degradation is insufficient causing a build-up of histamine in the body leading to symptoms.
What Causes Histamine Intolerance?
There are a number of possible causes of this condition:
- Genetic mutations – Genetic mutations can predispose you to become histamine intolerant. Some individuals have impaired production of the DAO and HNMT enzymes due to genetics. Those who have an MTHFR gene mutation are likely candidates for histamine intolerance because the mutation inhibits our ability to methylate properly, a process by which many toxins, including excess histamine, is eliminated. SNPs in MAO and PEMT genes can also cause this condition. Dr. Ben Lynch is an expert in this area of study.
- Mast cell activation disorder– Histamine lives in our mast cells (white blood cells). Mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS) is one type of mast cell activation disorder (MCAD) and is an immunological condition in which mast cells inappropriately and excessively release chemical mediators. It is usually caused by changes (mutations) in the KIT.
- Too much histamine-rich food– Certain foods are high in histamine. The amount of histamine we consume impacts the histamine level in our body. Fermented foods, high protein intake, aged foods, leftovers, citrus, fish are naturally high in histamine. You will find detailed information about these here.
- DAO inhibitors – Certain foods such as alcohol, green tea, and certain energy drinks lower DAO (the enzyme that breaks down histamine) function in the body. These foods increase histamine levels by impeding DAO’s effectiveness.
- Gut dysfunction / leaky gut / IBD– When the gut wall is damaged and leaky, the body’s ability to produce DAO is diminished. Poor gut health is a key reason for histamine intolerance.
- SIBO / dysbiosis – Bacteria, candida and other pathogens can produce large amounts of histamine as part of their metabolism.
- Nutrient deficiencies – Lack of vitamins/minerals such as B12, folate, B6, B2, B1, Zn, Cu, C, methionine can inhibit DAO production
- Medications – antibiotics, antacids and even antihistamines (long term) can deplete DAO levels in the body
- Nutrient demands – stress, anxiety, lack of sleep
- Hormonal insufficiency – adrenal fatigue
- Hormonal excess – Excess or even lowe levels of Oestrogen especially in women make them more susceptible to histamine intolerance
Symptoms
There is a broad spectrum of symptoms associated with this condition making it extremely hard to diagnose. Symptoms vary depending on the source of histamine when the total body level exceeds the enzymes’ capacity to break it down.
In some cases, symptoms are similar to an allergic reaction, but allergy tests usually come back as negative. You could experience one or many of the following symptoms after having a meal. It could be immediately after a meal or it may take a few hours or even days to surface as it could accumulate in your body.

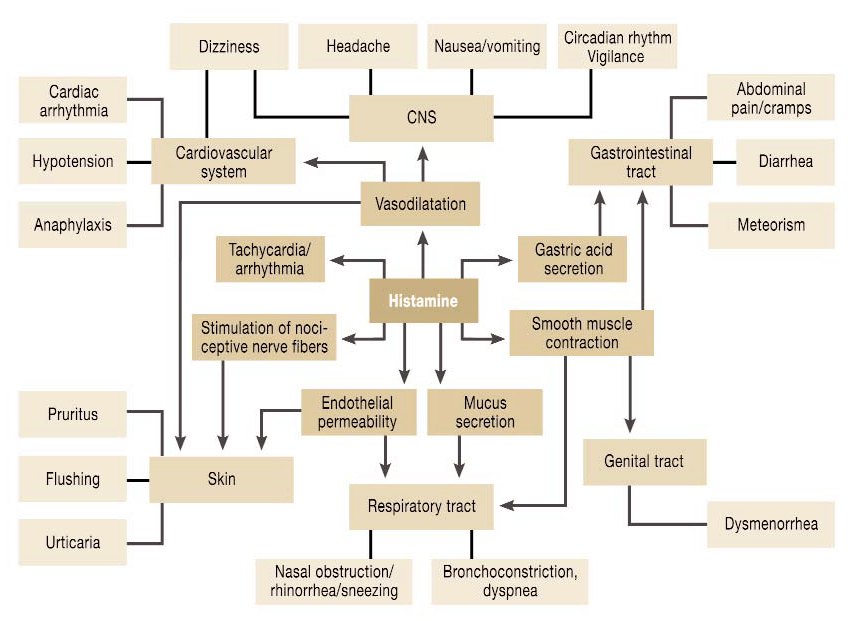
source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5346110
Most common symptoms of histamine intolerance include the following:
- Abdominal pain
- Migraines
- Irritability
- Excessive sweating when barely exercising
- Sweaty feet
- Nosebleeds
- Flushing: red face/red hot ears
- Exercise-induced asthma
- Insomnia
- Anxiety
- Dizziness
- Seasickness
- Eczema
Dr. Chris Kresser on “What you Should Know About Histamine Intolerance”
Testing for Histamine Intolerance
- Elimination – Even though there are many tests out there these days, according to the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, the gold standard is an elimination diet. This is performed by removing high histamine foods for 30 days and then slowly re-introducing them one at a time. If your symptoms resolve then you most likely have histamine intolerance. We tried this approach along with the skin prick testing on my children.
- Blood Testing –Certain companies offer a blood test to check for DAO If a DAO deficiency is detected you will be unable to break down histamine in your body. If testing is unavailable to you, you could simply try a diet low in histamine and add DAO supplementation at each meal. If your symptoms resolve, you could have low DAO.
- Skin Prick testing – According to research by Lukas, Heinz and Hanno a skin prick test is also presented to be effective. In this test the positive control is a histamine-containing solution. In general, the weal size of the histamine control would reduce within 20 minutes, but in individuals who are histamine intolerant, it will be visible even after an hour. My son performed this test (and was tested positive) at the National University Hospital in Singapore.
- Genetic testing – A genetic test such as 23andme or Ancestry.com could give you a good indication of the SNPs that may indicate a predisposition to histamine intolerance. However, having a predisposition means you have an increased risk of developing the condition, therefore, test results should be used along with symptoms to make a diagnosis. It is not always that one expresses their genetic predisposition.
- IgA and IgE testing – MRT and ALCAT are two popular methods of testing in the market today. This is a topic that is rapidly changing due to technological advances. You can read more about these tests in my article on allergy, intolerance testing
How to Reduce Histamine in the Body
As a first step, it is important to clear the histamine that gets accumulated in the body and stabilise mast cells and control the release of histamine naturally.
Stabilise Mast Cells
As histamine is released by mast cells it is important to look into stabilising your mast cells. If mast cells keep dumping histamine into the body it will just keep increasing your histamine levels. These antihistamine foods will help stabilise mast cells and control the release of histamine (5).
- Pea Sprouts – Will provide the most natural DAO. You can sprout them yourself or buy them already sprouted
- Blueberries – Are little antioxidant dynamos that also stabilize mast cells
- Parsley – Is rich in Luteolin and Quercetin. Both are mast cell stabilizers and h1/h2 antihistamines. Parsley also boasts a good amount of Vitamin C, A, calcium, magnesium and potassium.
- Cucumbers – Contain good amounts of magnesium and potassium which both help stabilize mast cells.
- Pomegranate – Contains Ellagic Acid which is great for mast cell stabilization.
- Red Onions – have a good amount of Quercetin
- Apples – are rich in antioxidants and is an antihistamine. Apples also contain Quercetin and Vitamin C that combat mast cells and histamine.
- Ginger – is an H1 and H2 antihistamine, mast cell stabilizer, anti-anaphylactic and boosts DAO.
- Celery – is rich in Luteolin which Is another great stabilizer and anti-inflammatory food.
- Fennel – is one of the top foods for providing Quercetin and is also high in Magnesium
- Kale – is a good source of Vitamin C, Kaempferol and Quercetin. All notable antihistamines and mast cell stabilizers. It’s a powerhouse of nutrition too with lots of Vitamin A, B6, to help create DAO. It is also packed with iron, magnesium and calcium.
- Moringa – Packs a lot of nutrition, including iron, is an antihistamine, stabilizes mast cells, is an anti-inflammatory and is liver protective. It is a good source of potassium and high in vitamin C.
- Chamomile Tea – Is another powerhouse that boosts DAO. It is an h1, h2 antihistamine and mast cell stabilizer. It is very helpful in alleviating digestive issues and promoting relaxation
Toxin Binders
Toxin binders are insoluble fibres that bind toxins in the body. When you are unable to metabolize certain toxins taking a binder will help, It simply binds up histamine in the gastrointestinal tract, hides histamine away from the body and directly eliminates it via the stool. It bypasses the DAO, HNMT, and MAO regulatory systems altogether. Taking a binder will relieve the stress on the liver. This was one of the first things that helped me, at-least until I got the situation under control.
Binders such as Zeolite have been found to effectively absorb excess histamine. Zeolite brands such as Toxa Prevent by FROXIMUN and COSEVA advanced TRS have proven to be very effective. Allison Vickery has a great article on binders and its usage here.
Histamine Intolerance Food List
Anyone who is histamine intolerant and very sensitive needs to be on a low histamine diet for a while. Avoiding high and moderately high, histamine foods allows bodily functions to catch up on degrading histamine. Once symptoms have reduced slowly adding histamine foods back is important too. But it cannot be done if the histamine bucket is overflowing. It takes a while to break down a histamine overload. Dietary changes make one of the biggest impact when trying to recover from an histamine overload.
My histamine food guide can be found here.
Adopt a Rotation Diet
Rotation diets (6) are widely recommended for people suffering from food sensitivities. The rationale of the rotation diet is that it takes 4 days for the immune system and particularly the villi to recoup itself. The diet works on food families rather than individual foods. If the family of foods is removed for 4 days then the gut will respond positively when challenged by that food family.
The benefit of a rotation diet is to help heal your gut by removing “reactive” foods which helps to reduce the inflammation and aids in healing. In addition, rotating the foods you can eat helps reduce new sensitives and allergies from occurring. For more information on rotation diet take a look at this article from Imupro.
We have had great success once we started on a rotation diet. In fact this is one of the things I wish we had tried sooner rather than later.
Control Histamine Producing Bacteria
The gut microbiome plays and important role in our digestive system. If there are imbalances in the microbiome histamine symptoms are likely to increase. The histamine content of foods increases over time as a result of microbial fermentation. This process is facilitated by some species of bacteria found in the gut that produce histamine:
- Lactobacillus species: Lactobacillus Bulgaricus, Lactobacillus Casei, Lactobacillus Delbrueckii, Lactobacillus Lactis, and Lactobacillus Reuteri
- Enterococcus species: Enterococcus Faecalis, and some types of Coli
- Klebsiella
- Enterobacter and Citrobacter
Consume Histamine Lowering Probiotics
In order to maintain the balance there are also certain types of bacteria or probiotics that degrade histamine. If the histamine producing bacteria proliferates and outnumbers the histamine-degrading bacteria, histamine build up occurs. This overwhelms the ability of the histamine degrading bacteria to breakdown the excess histamine which causes the symptoms of histamine intolerance to appear.
Histamine-lowering probiotics include:
- Bifidobacteriaspecies: particularly Bifidobacterium Infantis.
- Lactobacillus species: Lactobacillus Gasseri, Lactobacillus Plantarum, Lactobacillus Rhamnosus, and Lactobacillus Salivarius
You can check out my article on histamine reducing probiotics here.
Address Nutritional Imbalances
Several vitamins and minerals are necessary for the proper activity of DAO. Magnesium is an important cofactor in the production of DAO and magnesium deficiency may result in decreased DAO activity and excess histamine levels. Copper, Vitamin B6 and Vitamin C are other important DAO cofactors.
People with histamine intolerance may benefit from including more foods and drinks rich in these nutrients in their diet. You can take supplements if it is too difficult to get some nutrients because of low-histamine diet restrictions. Vitamins and minerals that are good for people with histamine intolerance include:
- Vitamin B-6, which helps DAO break down histamine
- Vitamin C to help lower histamine blood levels and help DAO break down histamine
- Copper, which helps raise DAO blood levels slightly and helps DAO break down histamine
- Magnesium that can raise the allergic response threshold
- Manganese that can enhance DAO activity
- Zinc to help DAO break down histamine (it may also have anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic properties)
- Calcium to help reduce hives and skin flushing
- Vitamin B-1
- Vitamin B-12
- Folic acid
Other Treatment Options
Address Underlying Causes
IF simply lowering/controlling your histamine levels does not work, it is possible that there is an underlying root cause that has given rise to your histamine sensitivity.
Methylation
Methylation is the process of adding a methyl group to a compound in your body, resulting in a specific action. Genetic variants, otherwise known as Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) can cause the MTHFR (methyltetrahydrofolate reductase) gene, which is responsible for methylation to not work as well. Methyl groups are supposed to bind to a receptor site on a substance like histamine and then breaks it down and excretes it from the body. Without enough methyl groups, histamine doesn’t get broken down very effectively. So if you have a SNP that affects methylation you can change your diet and life style to support and balance your body.
Foods to Support Methylation
There are certain low histamine foods that are able to help support and balance methylation in the body (7). Curcumin (from turmeric), quercetin (red onions), sulforaphane (broccoli), luteolin (chamomile), lutein (kale) and rosmarinic acid (rosemary).
Green leafy vegetables are especially important to include as they help get your daily intake of naturally occurring folate rather than folic acid. It is important to note that people who have the MTHFR mutation find it difficult to break down folic acid. Include in your diet low oxalate, low histamine greens like bok choy, lettuce, green/white cabbage, turnip greens, arugula, kale, kohlrabi leaves and watercress.
You can check out my article on methylation and its effects on histamine here.
Lifestyle to Support Methylation
Chronic or traumatic stress may cause negative changes in a person’s methylation ability. So, in general, a low-stress lifestyle that supports detoxification will help promote methylation and lower levels of histamine. Meditation and yoga are two stress relieving activities to incorporate in to your life style
Leaky Gut
If a person is unable to breakdown histamine and it keeps accumulating it can cause gut permeability or leaky gut. This is where the gut lining or villi gets damaged/inflamed and food particles pass through and get into your blood stream. When this occurs people start reacting to not only high histamine food but practically everything they eat. Effectively improving your leaky gut by taking gut healing supplements such as L-Glutamine and Slippery elm as well as controlling the diet will give you relief. Tests to confirm leaky gut Comprehensive digestive stool analysis.
Mold
Mold has become a major trigger and cause of histamine intolerance in recent times. Especially for people suffering from Mast Cell Activation Syndrome mold is a common trigger. Eliminate yourself from mold exposure, use toxin binders and stabilse your mast cells with a low histamine diet and mast cell stabilising food.
SIBO (Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth)
According to Amy Myers MD, SIBO can be an underlying cause of histamine sensitivity. SIBO causes the gut to be inflammed which in turn impairs DAO production. It is also known that the bacteria that has over-grown in the small intestines will start producing histamine as part of their metabolism which then adds to the histamine bucket. If you suspect SIBO, it is important to get tested for it and start on a plan to heal SIBO.
Take Suitable Supplements
Although I am not a fan of too many supplements, at times it is necessary to take some supplements at-least for a certain period.
If you are struggling with food intolerances or other digestive problems, there are products that can help YOU. This list has been compiled through my own experience as well as working together with trusted and experienced practitioners worldwide
Click to Get My Recommended Supplements ListRelated Conditions
Many who have histamine intolerance have shown symptoms of salicylate intolerance and glutamate intolerance as well. Both my kids have these 3 conditions.
Disclaimer: The content provided in this article, and in any linked materials, are not intended and should not be construed as medical advice. If the reader or any other person has a medical concern, he or she should consult with an appropriately licensed physician or certified health care worker who can provide personalised advice.
References
- What is Histamine, Wikipedia. Link here https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Histamine
- Histamine Intolerance, Healthline. Link here https://www.healthline.com/health/histamine-intolerance
- What are Histamines, Webmed. Link here https://www.webmd.com/allergies/what-are-histamines#1
- Are you Suffering from Histamine Intolerance, Dr. Jockers. Link here https://drjockers.com/suffering-histamine-intolerance/
- D F Finn and J J Walsh, Twenty first century mast cell stabilizers, PMID: 23441583. Link here https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3764846/
- The Rotation Diet, Alison Vickery. Link here. https://alisonvickery.com.au/the-rotation-diet/
- Romilly E. Hodges 1 and Deanna M. Minich, Modulation of Metabolic Detoxification Pathways Using Foods and Food-Derived Components: A Scientific Review with Clinical Application, PMID: 26167297. Link here https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4488002/